Difference Between Connotative and Denotative Meanings with Examples-Grammar Puzzle Solved-31
Language carries meaning on many levels. Words not only define objects or concepts but also suggest emotions and cultural associations. This is where connotative and denotative meanings come into play. Understanding the difference between them helps in interpreting texts more accurately, whether in literature, conversation, or academic writing.
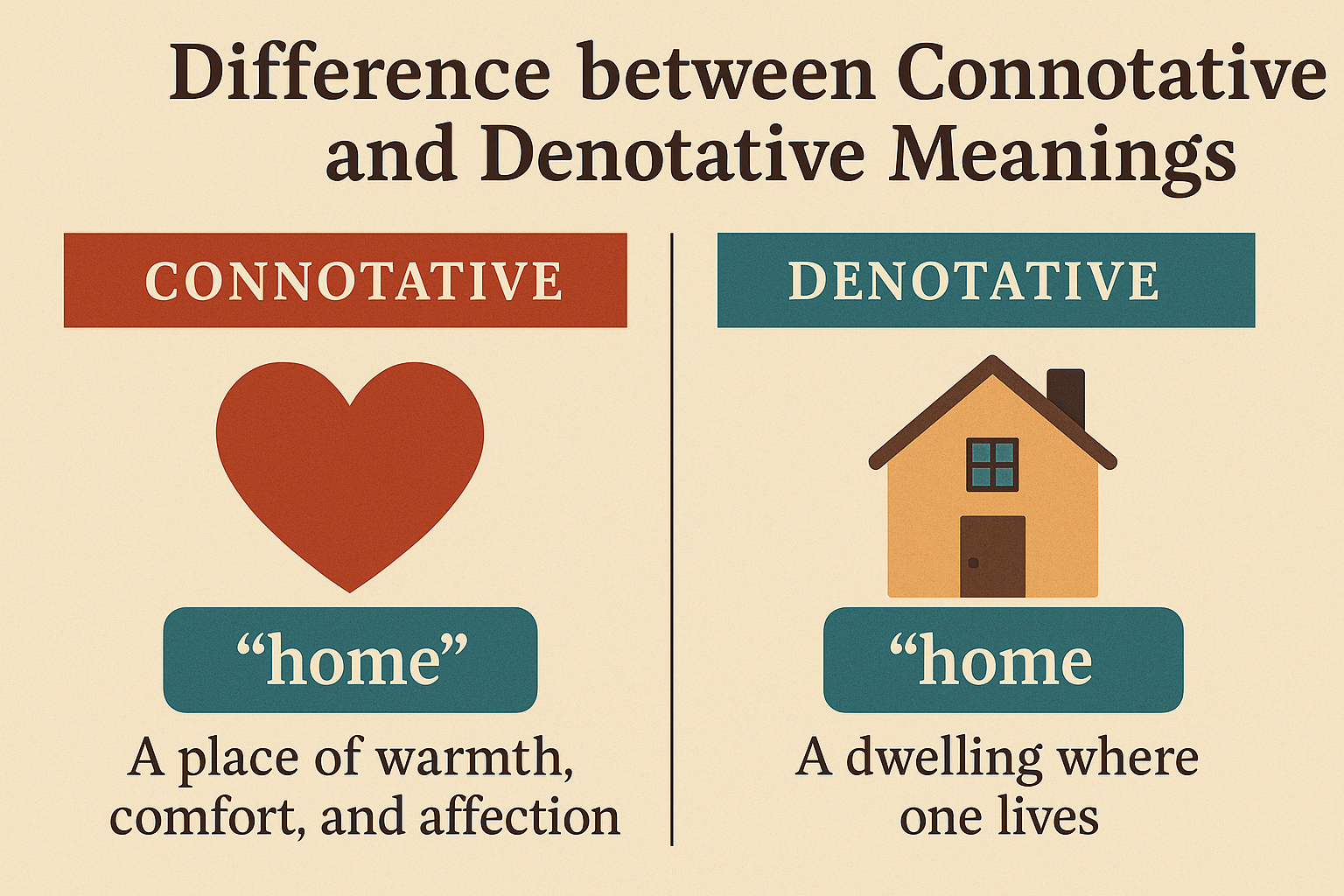
What Are Denotative Meanings?
Denotative meanings refer to the literal or dictionary definitions of a word. They are objective and do not change based on context or emotion. For example:
- Dog (denotative): A domesticated mammal that barks.
- Rose (denotative): A type of flower with thorny stems.
These definitions remain constant regardless of how people feel about the words. They provide the most basic, universally accepted understanding.
What Are Connotative Meanings?
Connotative meanings, on the other hand, are emotional or cultural associations connected with a word. They go beyond the dictionary and tap into the personal or social ideas people attach to language. For instance:
- Dog (connotative): Loyalty, protection, or even insult (when used negatively).
- Rose (connotative): Love, passion, or romance.
Different audiences may interpret connotative meanings differently. While the denotative meaning of a “snake” is a legless reptile, the connotative meaning might include ideas like danger, betrayal, or evil.
Key Differences Between Connotative and Denotative Meanings
To clearly understand the difference between connotative and denotative meanings, consider these points:
- Objectivity vs. Subjectivity
- Denotative meanings are objective and fixed.
- Connotative meanings are subjective and can vary.
- Context
- Denotative meanings remain the same in any context.
- Connotative meanings depend on the situation, tone, or cultural background.
- Use in Literature and Media
- Writers use connotative meanings to add depth.
- Dictionaries list only denotative meanings.
More Examples of Denotative and Connotative Meanings
Here are additional examples to highlight the difference between connotative and denotative meanings:
| Word | Denotative Meaning | Connotative Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Home | A place where someone lives | Comfort, family, security |
| Cheap | Low in cost | Low quality, stingy |
| Childish | Like a child | Immature, silly |
| Dove | A type of bird | Peace, innocence |
| Night | Time between sunset and sunrise | Darkness, fear, mystery |
These examples show how the same word can have different implications based on emotional or cultural factors.
Why the Difference Matters
Knowing the difference between these two is essential for clear communication. Advertisers, poets, and speakers rely on connotations to create strong emotional responses. Misunderstanding a connotation may lead to confusion or miscommunication.
For instance, calling someone a “snake” in a literal sense might just refer to the animal, but in many cultures, it implies deception. Similarly, labeling a product “cheap” could either be a selling point or a criticism, depending on the intended meaning.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both connotative and denotative meanings play a vital role in language. The difference between connotative and denotative meanings lies in emotion versus fact, or association versus definition. By understanding this distinction, you can become a more effective communicator and a better reader of texts. Always pay attention to how words are used, especially when they seem to carry emotional weight.
Ezra Pound as a Modernist Writer:
https://englishlitnotes.com/2025/05/30/ezra-pound-modernist-writer/
Notes on English for All Classes: https://englishwithnaeemullahbutt.com/
Grammar Puzzle Solved: https://grammarpuzzlesolved.englishlitnotes.com/category/grammar-puzzle-solved-by-naeem-sir/
For English and American literature and grammar, visit Google:https://www.google.com
Discover more from Grammar Puzzle Solved by Naeem Ullah Butt
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.